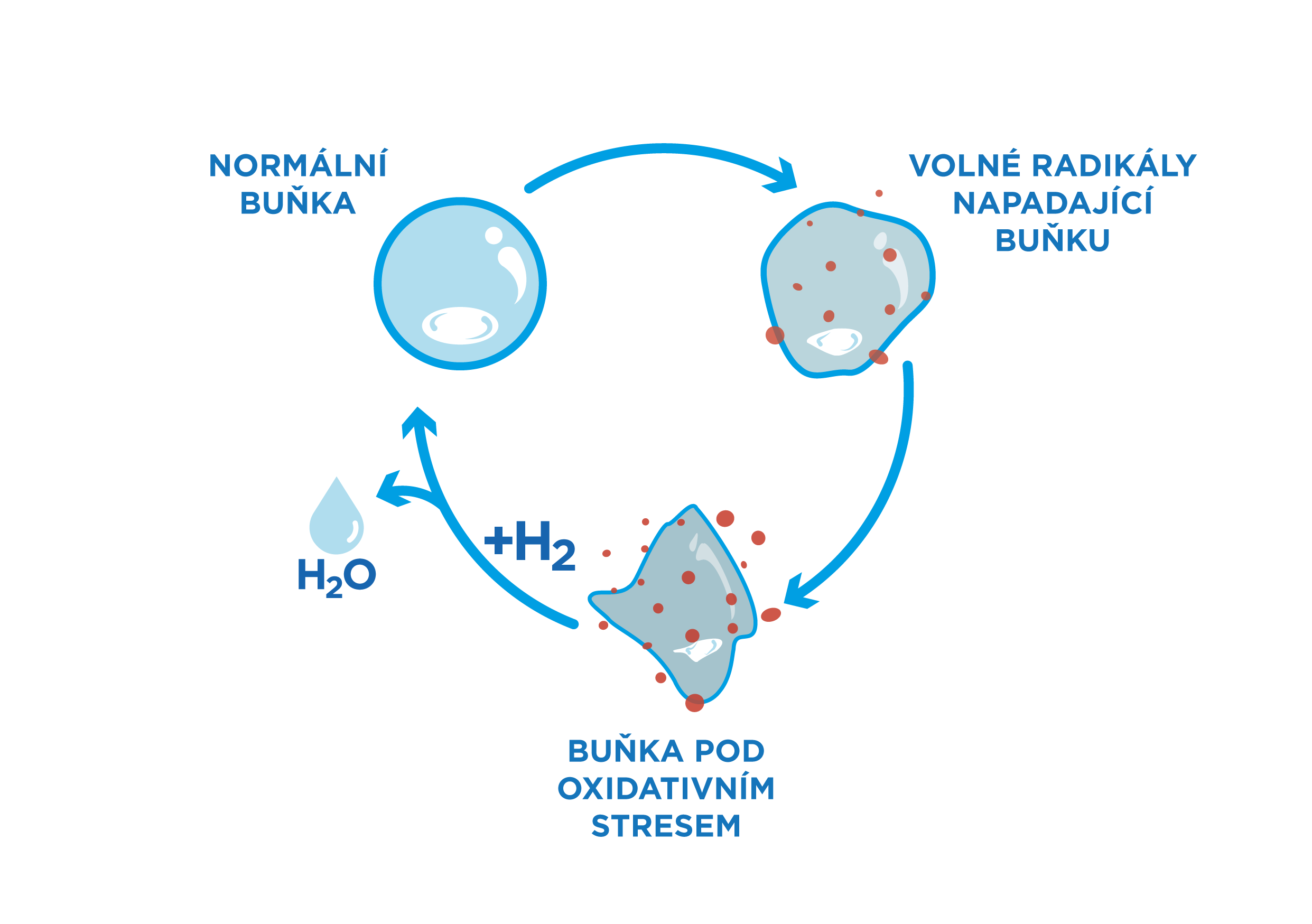
Antioxidants are substances that help protect our bodies from the harmful effects of free radicals. These are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer or diabetes. Molecular hydrogen appears to be an ideal source of antioxidants. The smallest molecule that can provide significant health benefits and promote quality and long life.
How do antioxidants work?
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals by providing them with electrons, which stabilizes the free radicals and prevents them from damaging cells. This process helps maintain balance in the body and protects cells from oxidative stress, which is associated with many health problems and aging.
Why do we need antioxidants?
- Protection from disease: antioxidants can reduce the risk of chronic disease.
- Immune system support: They help maintain a healthy immune system, which is key to fighting infections.
- Slow aging: Protecting cells from damage can slow the aging process.
- Support recovery: They help the body recover faster after physical exertion and stress.
The five most powerful antioxidants
- Vitamin C: One of the most well-known antioxidants that supports the immune system and helps in tissue regeneration. It is found in citrus fruits, peppers and strawberries, for example.
- Vitamin E: Protects cell membranes from damage and promotes skin health. It can be found in nuts, seeds and green leafy vegetables.
- Beta-carotene: A precursor to vitamin A that supports eye and immune system health. It is abundant in carrots, sweet potatoes and spinach.
- Flavonoids: Powerful antioxidants found in fruits, vegetables, tea and chocolate. They have anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects.
- Molecular hydrogen: The smallest and most powerful antioxidant that can easily penetrate cells and protect them from oxidative stress. Molecular hydrogen has the potential to improve energy levels and promote overall health.
Molecular hydrogen (H2) is a unique antioxidant that, due to its small size, can penetrate cells and directly neutralize free radicals at the mitochondrial level. Studies show that molecular hydrogen has powerful anti-inflammatory effects and can help protect organs from damage caused by oxidative stress.